
[Experimental study] Effects of dietary supplementation of biosurfactant peptide | on growth, lipid metabolism and digestive enzyme activities of California bass
Abstract: This study was to evaluate the effects of Esurfier on growth, health and intestinal digestive enzyme activity of California bass, and to provide theoretical basis for dietary cost reduction and efficiency improvement. Six groups of isonitrogen feed were designed. They were: high fish meal high fat (HH), low fish meal high fat (LH), low fish meal low fat (LL0), low fish meal low fat +0.02% Esurfier (LL2), low fish meal low fat +0.04%Esurfier (LL4), low fish meal low fat +0.06% Esurfier (LL6), with 6 replicates per group. Each group had 6 replicates , 30 fish per replicate. The experiment lasted for 10 weeks. The results showed that the addition of 0.04% Esurfier to reduce 10 kg of oil per ton could significantly improve the weight gain rate and reduce the feed coefficient of California bass. The serum high density lipoprotein cholesterol content was significantly increased and low density lipoprotein cholesterol content was decreased. The liver fat content was significantly decreased, the gene expression of hepatic fatty acid synthetase FAS was inhibited, and the gene expression of CPT1α, a key fatty acid oxidation enzyme, was up-regulated. The activity of lipase and trypsin in digestive tract was significantly improved.
Key words: emulsifier; Biosurfactant peptide; Growth performance; Lipid metabolism; Digestive enzyme
1 Purpose
To evaluate the effects of Esurfier on growth, health and intestinal digestive enzyme activity of California bass, and provide theoretical basis for reducing feed cost and increasing feed efficiency
2 Trial methods
2.1 Trial material
Esurfier, produced by Beijing Enhalor Biotechnology Co., LTD., consists of biosurfactant peptide and glycerol monostearate.
2.2 Trial method
This experiment designed 6 groups of isonitrogenous feeds, namely HH ( 44 % fish meal, 12.95 % crude fat), LH ( 36 % fish meal, 12.92 % crude fat), LL0 ( 36 % fish meal, 11.92 % crude fat), LL2 (HL0 + 0.02 % Esurfier), LL4 (HL0 + 0.04 % Esurfier), and LL6 (HL0 + 0.06 % Esurfier). A 10- week breeding experiment was conducted.
2.3 Experimental grouping and breeding management
The experiment was conducted in the indoor recirculating aquaculture system of the Biotechnology Research Institute of Beijing Enhalor Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Before the formal start, the fish were temporarily kept in the aquaculture system for 2 weeks, control group feed was fed during the temporary period. California bass with healthy physique and uniform individuals (initial weight: 7.63 g) were randomly selected. Each treatment had 6 replicates, 30 fish in each replicate, a total of 36 aquaculture barrels. Each aquaculture barrel was fed twice a day, the aquaculture cycle was 10 weeks. The daily feeding amount was recorded.
2.4 Data analysis
The experimental data were expressed as mean ± standard error, one-way analysis of variance was used for data analysis (SPSS 17.0). When there was a significant difference, Duncan's method was used for multiple comparisons, and P < 0.05 was considered a significant difference.
3 Results
3.1 Effects of Esurfier on growth and feed efficiency of California bass
0.04 % Esurfier to the LL0 (36 % fish meal, 11.92 % crude fat) feed significantly promoted the California bass growth (Table 2, P < 0.05), and its growth was better than that of the HH group (44 % fish meal, 12.95 % crude fat); 0.02 % -0.04 % Esurfier significantly improved the feed efficiency of California bass (P < 0.05), the feed coefficient dropped from 0.91 to 0.88-0.89. The survival rate of each group was 100 % (P > 0.05).
3.2 Effects of Esurfier on body parameters of California bass
Esurfier had no significant effect on the fullness, viscerosomatic index, hepatosomatic index, and abdominal fat rate of California sea bass (Table 3, P > 0.05).
3.3 Effects of Esurfier on serum lipid metabolism of California bass
Esurfier significantly increased the content of "good cholesterol" HDL-C (Table 4, P < 0.05), reduced the content of "bad cholesterol" LDL -C (P < 0.05), had no significant effect on the serum TG and TC levels of California seabass (P > 0.05).
3.4 Effects of Esurfier on lipid metabolism in California bass hepatopancreas
There was no significant difference in hepatosomatic TG and TC contents among the groups (Table 5, P > 0.05). Esurfier significantly reduced the crude fat content in the fish hepatopancreas (Figure 1, P < 0.05). As shown in Figure 2, Esurfier significantly inhibited the gene expression of fatty acid synthase FAS, of which the LL4 and LL6 groups were significantly lower than the LL0 group (P < 0.05). In addition, the gene expression of the key enzyme of fatty acid oxidation CPT1α in the LL6 group was significantly upregulated (P < 0.05). This showed that Esurfier improved lipid metabolism of California bass by inhibiting fatty acid synthesis and promoting fatty acid oxidation.
Table 1 Feed formula
HH | LH | L0 | L L2 | L4 | L6 | |
Imported super fish meal | 44.00 | 36 .00 | 36 .00 | 36 .00 | 36 .00 | 36 .00 |
Pet Grade Chicken Meal | 12.00 | 1 4 .00 | 1 4 .00 | 1 4 .00 | 1 4 .00 | 1 4 .00 |
Cottonseed Protein Concentrate | 9.3 0 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 15.00 |
Soybean meal | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
Gluten | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 |
flour | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 |
Cassava starch | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
Microcrystalline cellulose | 2.10 | 1.90 | 2.90 | 2.88 | 2.86 | 2.84 |
Calcium dihydrogen phosphate | 1.70 | 1.80 | 1.80 | 1.80 | 1.80 | 1.80 |
Choline chloride | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
Premix | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
Fish oil | 2.4 0 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
Soybean oil | 5.2 0 | 5.0 0 | 4.0 0 | 4.0 0 | 4.0 0 | 4.0 0 |
Esurfier | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
Total | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
Crude Protein | 49.99 | 49.86 | 49.86 | 49.86 | 49.86 | 49.86 |
Crude fat | 12.95 | 12.92 | 11.92 | 11.92 | 11.92 | 11.92 |
Table 2 Effects of Esurfier on growth and feed efficiency of California bass
HH | LH | L0 | L L2 | L4 | L6 | |
WGR (%) | 998±10.7ab | 983±19.3ab | 970±21.7b | 995±14.2ab | 1032±20.0 a | 1004±16.5ab |
SGR (% day -1 ) | 3.52±0.0ab | 3.50±0.03ab | 3.49±0.03b | 3.52±0.02ab | 3.57± 0.03a | 3.53±0.02ab |
FR (% bw day -1 ) | 2.11±0.02d | 2.15±0.01cd | 2.23±0.01a | 2.16±0.01bc | 2.19±0.01ab | 2.21±0.02 a |
FCR | 0.86±0.01d | 0.88±0.01cd | 0.91±0.01a | 0.88±0.01cd | 0.89±0.01bc | 0.90±0.01ab |
SR ( % ) | 1 00±0.00 | 1 00±0.00 | 1 00±0.00 | 1 00±0.00 | 1 00±0.00 | 1 00±0.00 |
WGR = 100 × (final weight - initial weight) / initial weight
SGR = 100 × (LN (final average weight) - LN (initial average weight)) / number of days
FR = 100 × feed intake/ [(initial fish weight + final fish weight)/ 2]/ days
FCR = feed intake/ (final fish weight - initial fish weight)
SR = 100 × final number of fish/initial number of fish
Table 3 Effects of Esurfier on body parameters of California bass
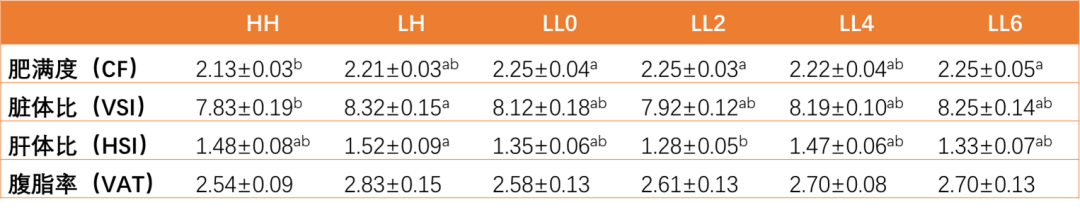
CF = 100 × body weight/body length3
VSI = 100 × visceral weight / body weight
HSI = 100 × hepatosomatic weight / body weight
VAT = 100 × abdominal fat weight / body weight
Table 4 Effects of Esurfier on serum lipid metabolism of California bass
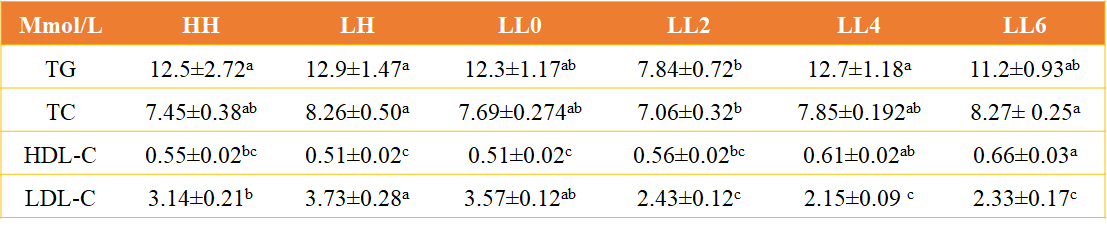
Table 5 Effect of Esurfier on TG and TC contents in the California bass hepatopancreas
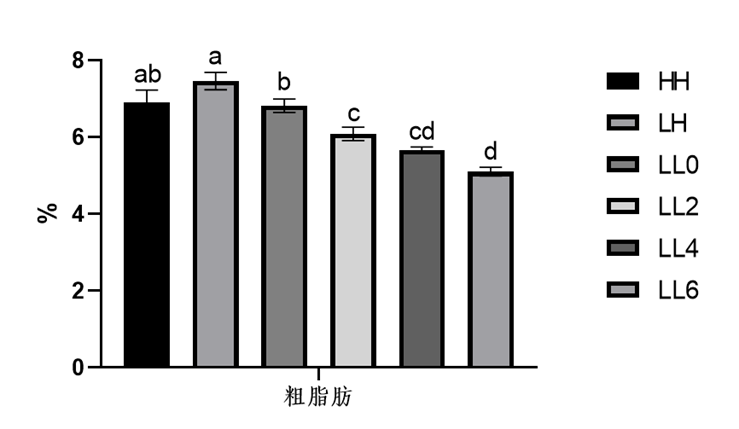
Figure 1 Effect of Esurfier on crude fat content in California bass hepatopancreas
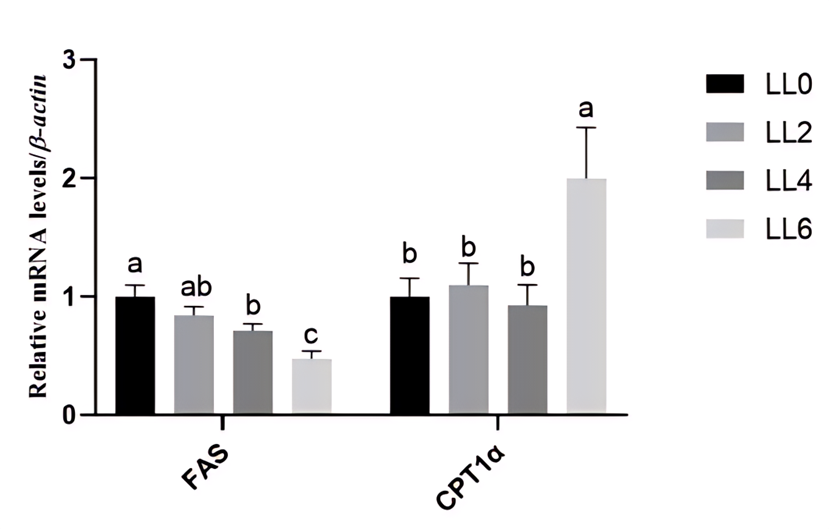
Figure 2 Effect of Esurfier on the expression of FAS and CPT1α genes in California bass hepatopancreas
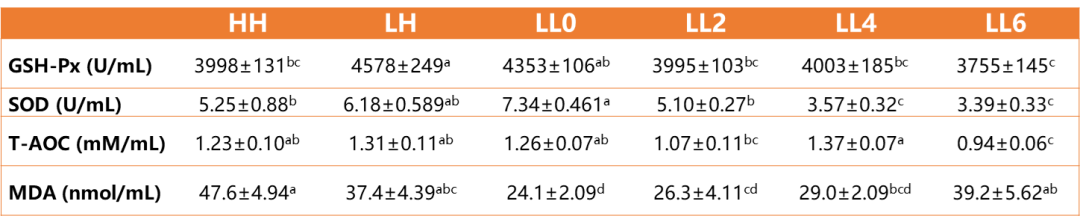
3.5 Effects of Esurfier on serum antioxidant indexes of California bass
As shown in Table 6, compared with the LL0 group, the serum GSH-Px, T -AOC, and SOD activities of California seabass in the LL6 group decreased significantly, and the MDA content increased significantly.
Table 6 Effects of Esurfier on serum antioxidant indexes of California bass
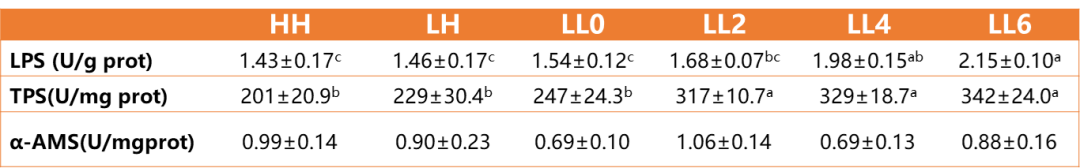
3.6 Effects of Esurfier on intestinal digestive enzyme activities of California bass
As shown in Table 7, the lipase activity in the LL4 and LL6 groups was significantly higher than that of the HH, LH, and LL0 groups (P < 0.05). The trypsin activity in the LL2, LL4, and LL6 groups was significantly higher than that of the HH, LH, and LL0 groups (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in α-AMS activity among the groups (P > 0.05).
Table 7 Effects of Esurfier on intestinal digestive enzymes of California bass
4 Conclusion
In the diet of California bass, adding 0.04% Esurfier to reduce 10 kg of oil per ton could significantly improve the weight gain rate and reduce the feed coefficient. The serum high density lipoprotein cholesterol content was significantly increased and low density lipoprotein cholesterol content was decreased. The liver fat content was significantly decreased, the gene expression of hepatic fatty acid synthetase FAS was inhibited, and the gene expression of CPT1α, a key fatty acid oxidation enzyme, was up-regulated. The activity of lipase and trypsin in digestive tract was significantly improved.
EsurfierTM
Esurfier is a feeding emulsifier developed by the Enhalor Biotechnology Research Institute in Beijing and the Department of Chemical Engineering at Tsinghua University. Its core component is a microbial lipid produced by the fermentation of the patented strain Bacillus subtilis, biosurfactant peptide (subtilis surfactant peptide), which is one of the most surfactants reported so far. The emulsification and emulsification stability of Esurfier exceed that of conventional emulsifiers, promoting greater fat digestion ability. In addition, the unique parental structure of Esurfier's core components accelerates the absorption of lipids. The use of Esurfier in feed can improve the production performance of animals, improve the health level and reduce the feed cost.





 China
China 
